You are here: Home > Section on Cellular and Developmental Biology
Genes and Signals Regulating Mammalian Hematopoiesis

- Paul Love, MD, PhD, Head, Section on Cellular and Developmental Biology
- Dalal El-Khoury, BS, Technician
- SuJin Hwang, PhD, Visiting Fellow
- Jan Lee, BS, Technician
- Renaud Lesourne, PhD, Visiting Fellow
- LiQi Li, MD, PhD, Research Fellow
- Julia Pinkhasov, PhD, Postdoctoral Fellow
- Ekaterina Zvezdova, PhD, Visiting Fellow
Our research focuses on the development of the mammalian hematopoietic system. Of particular interest to our laboratory is the characterization of signal transduction molecules and pathways that regulate T cell maturation in the thymus. Current projects include the generation of transgenic and conditional deletion mutants to evaluate the importance of T cell antigen receptor signaling at specific stages of T cell development. We are also using Microarray gene profiling to identify molecules that are important for thymocyte selection, a process that promotes the survival and development of functional T cells and the death of auto-reactive T cells. A recently initiated area of investigation focuses on hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). We have begun to characterize the genes that are important for the generation and maintenance of HSCs and for their differentiation into specific hematopoietic lineages. These studies have revealed a critical function for one protein (Ldb1) in controlling the self-renewal/differentiation cell fate decision in hematopoietic stem cells.
T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling in thymocyte development
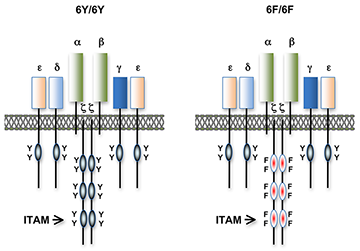
Figure 1. T cell antigen receptors expressed in 6Y/6Y and 6F/6F knock-in mice.
Subunit composition of the T cell antigen receptors in 6Y/6Y and 6F/6F mice. 6Y/6Y mice express wild-type zeta chain dimers with functional ITAM signaling motifs that contain two tyrosine (Y) residues. 6F/6F mice express mutant zeta chain dimers in which the ITAM tyrosines have been changed to phenylalanine (F). (click image to enlarge)
Much of our research focuses on investigating the role of TCR signal transduction in thymocyte development. Signal transduction sequences (termed Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motifs; ITAMs) are contained within four distinct subunits of the multimeric TCR complex (zeta, CD3-gamma, CD3-delta, and CD3-epsilon). Di-tyrosine residues within ITAMs are phosphorylated upon TCR engagement; their function is to recruit signaling molecules, such as protein tyrosine kinases, to the TCR complex, thereby initiating the T cell activation cascade. Though conserved, ITAM sequences are nonidentical, raising the possibility that the diverse developmental and functional responses controlled by the TCR may be partly regulated by distinct ITAMs. We previously generated zeta-deficient and CD3-epsilon–deficient mice by gene targeting. We genetically reconstituted the mice with transgenes encoding wild-type or signaling-deficient (ITAM-mutant) forms of zeta and CD3-epsilon and characterized the developmental and functional consequences of these alterations for TCR signaling. We found that TCR-ITAMs are functionally equivalent but act in concert to amplify TCR signals. TCR signal amplification was critical for thymocyte selection, the process by which potentially useful immature T cells are instructed to survive and differentiate further (positive selection) and by which potentially auto-reactive cells that may cause auto-immune disease are deleted in the thymus (negative selection). Unexpectedly, we found that multiple TCR-ITAMs are not required for mature T cell effector functions. One possible explanation is that ITAM-mediated signal amplification is not required for mature T cell activation; another is that T cells in ITAM-mutant mice exhibit normal functional responsiveness because of compensatory mechanisms imposed during selection. To resolve this issue, we recently generated a TCR-zeta chain conditional knockin mouse in which T cell development and selection can occur without attenuation of TCR signaling (i.e., in the presence of wild-type 3 ITAM zeta chain), but in which mature, post-selection T cells may be induced to express TCRs containing signaling-defective (0 ITAM) zeta chains in lieu of wild-type zeta chain. Thus, mature T cell signaling should not be influenced by potential compensatory mechanisms that operate during T cell maturation such that T cells in these mice should be faithful indicators of the role of multiple TCR ITAMs in mediating specific, mature T cell responses. Preliminary experiments with the mice confirmed that the knockin zeta locus functions as predicted. We are currently using this model system to evaluate the role of ITAM multiplicity in mature T cells.
Identification and characterization of proteins important for TCR fine tuning and TCR signaling
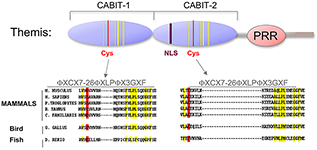
Figure 2. Themis is highly conserved in vertebrates
Themis contains two novel CABIT domains, each with a conserved cysteine (red) and conserved flanking residues (yellow), a nuclear localization signal (NLS), and Proline Rich Region (PRR). (click image to enlarge)
We have extended our analysis of TCR signaling subunits to other molecules that participate in or influence the TCR signaling response. The cell-surface protein CD5 negatively regulates TCR signaling and functions in thymocyte selection. Examination of CD5 expression during T cell development revealed that surface levels of CD5 are regulated by TCR signal intensity and by the affinity of the TCR for self-peptide ligands in the thymus that mediate selection. To determine if the ability to regulate CD5 expression is important for thymocyte selection, we generated transgenic mice that constitutively express high levels of CD5 throughout development. Overexpression of CD5 significantly impaired positive selection of some thymocytes (those that would normally express low levels of CD5) but not of others (those that would normally express high levels of CD5). These findings support a role for CD5 in modulating TCR signal transduction and thereby influencing the outcome of thymocyte selection. The ability of individual thymocytes to regulate CD5 expression represents a mechanism for “fine tuning” the TCR signaling response during development. Reasoning that other molecules besides CD5 participate in TCR tuning, we initiated microarray-based screening for genes differentially expressed in developing T cells under conditions of high- or low-affinity TCR interactions and have identified several candidate genes for further study.
Role of Ldb1 in T cell development
Lim domain binding protein-1 (Ldb1) is a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein that contains a LIM-zinc-finger–protein interaction motif and a dimerization domain. In hematopoietic cells, Ldb1 functions by interacting with and/or recruiting specific partners (including the LIM-only protein LMO2 and the transcription factors SCL and GATA-1,2) to form multimolecular transcription complexes. Within the hematopoietic lineage, expression of Ldb1 is highest in progenitors, which include hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Ldb1−/− mice die between day 9 and day 10 of gestation, preventing us from directly studying the impact of loss of Ldb1 on fetal or adult hematopoiesis. We investigated the role of Ldb1 in hematopoiesis by following the fate of Ldb1-null embryonic stem (ES) cells in mouse blastocyst chimeras and by conditional, stage-specific deletion of Ldb1. Significantly, Ldb1-null ES cells were capable of generating HSCs, which could give rise to both myeloid and lymphoid lineage cells; however, the number of Ldb1−/− HSCs gradually diminished at later stages of development. Following adoptive transfer of fetal liver cells, Ldb1-null HSCs were rapidly lost over a period of three months, indicating a failure of self-renewal or survival. More recent data indicate that the loss of Ldb1-null HSCs results from differentiation rather than cell death. Although expressed in ES cells, Ldb1 is not required for ES maintenance, indicating a selective requirement in adult stem cell populations. We performed a genome-wide screen for Ldb1 binding sites using ChIP-seq high-throughput sequencing. Analysis of ChIP-seq data revealed that Ldb1 binds at the promoter or regulatory sequences near a large number of genes know to be required for HSC maintenance. These data suggest that Ldb1 complexes may function in a manner similar to Oct4/nanog/Sox2 in ES cells to regulate a core transcriptional network necessary for stem cell maintenance.
Identification and characterization of Themis, a novel protein required for T cell development
Using a subtractive cDNA library–screening approach, we recently identified a novel T cell–specific protein, Themis. To investigate the function of Themis in T cell signaling and development, we generated Themis knockdown cell lines, Themis knockout mice, and Themis transgenic mice. Analysis of the effects of modulating Themis expression revealed a critical role for Themis in late T cell development. Surprisingly, no proximal T cell antigen receptor signaling defects were observed in Themis−/− thymocytes indicating that Themis functions at more distal points in the signaling pathway, perhaps by integrating or sustaining signaling. Current studies focus on elucidating the mechanism through which Themis regulates T cell development.
Role of Ldb1 in T cell development
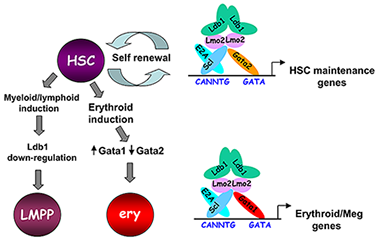
Figure 3. Model of Ldb1 function in the hematopoietic lineage.
Ldb1 forms a multimeric DNA binding complex in hematopoietic cells with the adapter Lmo2 and the transcription factors Scl and Gata1 or Gata2. In Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), in which Gata2 is highly expressed, Ldb1-Lmo2-Scl-Gata2 complexes positively regulate expression of HSC maintenance genes. Differentiation of HSCs to the myeloid or lymphoid lineage (LMPP) is trigged by downregulation of Ldb1 whereas commitment to the erythroid lineage (ery) is triggered by induction of Gata1 and downregulation of Gata2, resulting in the formation of an Ldb1-Lmo2-Scl-Gata1 complex that positively regulates expression of erythroid-specific genes. (click image to enlarge)
Lim domain binding protein-1 (Ldb1) is a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein that contains a LIM-zinc-finger protein interaction motif and a dimerization domain. In hematopoietic cells, Ldb1 functions by interacting with and/or recruiting specific partners (including the LIM-only protein LMO2 and the transcription factors SCL and GATA-1,2) to form multimolecular transcription complexes (Figure 3). Within the hematopoietic lineage, expression of Ldb1 is highest in progenitors, which include hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Ldb1−/− mice die between day 9 and 10 of gestation, preventing us from directly studying the impact of loss of Ldb1 on fetal or adult hematopoiesis. We investigated the role of Ldb1 in hematopoiesis by following the fate of Ldb1-null embryonic stem (ES) cells in mouse blastocyst chimeras and by conditional, stage-specific deletion of Ldb1. Significantly, Ldb1-null ES cells were capable of generating HSCs, which could give rise to both myeloid and lymphoid lineage cells; however, the number of Ldb1−/− HSCs gradually diminished at later stages of development. Following adoptive transfer of fetal liver cells, Ldb1-null HSCs were rapidly lost over a period of three months, indicating a failure of self-renewal or survival. More recent data indicate that the loss of Ldb1-null HSCs results from differentiation rather than cell death. Although expressed in ES cells, Ldb1 is not required for ES maintenance, indicating a selective requirement in adult stem cell populations. We performed a genome-wide screen for Ldb1 binding sites using ChIP-seq high-throughput sequencing. Analysis of ChIP-seq data revealed that Ldb1 binds at the promoter or regulatory sequences near a large number of genes know to be required for HSC maintenance. The data suggest that Ldb1 complexes may function in a manner similar to Oct4/nanog/Sox2 in ES cells to regulate a core transcriptional network necessary for stem cell maintenance. Examination of the function of Ldb1 in lineages downstream of the HSC identified an essential function in the erythroid lineage but not in other myeloid cells or lymphoid cells. Interestingly, ChIP-seq analysis of Ldb1 DNA binding complexes in erythroid cells demonstrated that Ldb1 complexes contained Gata1 (which is highly expressed in the erythroid lineage) instead of Gata2. The results suggest that multimeric Ldb1 transcription complexes may have distinct functions in the hematopoietic system depending upon their subunit composition, with Gata2-containing complexes regulating expression of HSC maintenance genes and Gata1 complexes regulating expression of erythroid-specific genes (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Model of Ldb1 function in the hematopoietic lineage.
Ldb1 forms a multimeric DNA binding complex in hematopoietic cells with the adapter Lmo2 and the transcription factors Scl and Gata1 or Gata2. In Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), in which Gata2 is highly expressed, Ldb1-Lmo2-Scl-Gata2 complexes positively regulate expression of HSC maintenance genes. Differentiation of HSCs to the myeloid or lymphoid lineage (LMPP) is trigged by downregulation of Ldb1 whereas commitment to the erythroid lineage (ery) is triggered by induction of Gata1 and downregulation of Gata2, resulting in the formation of an Ldb1-Lmo2-Scl-Gata1 complex that positively regulates expression of erythroid-specific genes. (click image to enlarge)
Publications
- Deford-Watts LM, Tassin TC, Becker AM, Medeiros JJ, Albanesi JP, Love PE, Wulfing C, van Oers NS. The cytoplasmic tail of the T cell receptor CD3 epsilon subunit contains a phospholipid-binding motif that regulates T cell functions. J Immunol. 2009 183:1055-1064.
- Lesourne R, Uehara S, Lee J, Song KD, Li L, Pinkhasov J, Zhang Y, Weng NP, Wildt KF, Wang L, Bosselut R, Love PE. Themis, a T cell-specific protein important for late thymocyte development. Nat Immunol. 2009 10:840-847.
- Tzchori I, Day TF, Carolan PJ, Zhao Y, Wassif CA, Li L, Lewandoski M, Gorivodsky M, Love PE, Porter FD, Westphal H, Yang Y. LIM homeobox transcription factors integrate signaling events that control three-dimensional limb patterning and growth. Development 2009 136:1375-1385.
- Hayes SM, Laird RM, Love PE. Beyond alphabeta/gammadelta lineage commitment: TCR signal strength regulates gammadelta T cell maturation and effector fate. Semin Immunol. 2010 22(4):247-251.
- Li L, Lee J, Gross J, Song S, Dean A, Love PE. A requirement for Lim domain binding protein in erythropoiesis. J Exp Med. 2010; in press.
Collaborators
- Avinash Bhandoola, PhD, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
- Joshua Farber, MD, Laboratory of Clinical Investigation, NIAID, Bethesda, MD
- Sandra M. Hayes, MD, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY
- Alfred Singer, MD, Experimental Immunology Branch, NCI, Bethesda, MD
- Heiner Westphal, MD, Program on Genomics of Differentiation, NICHD, Bethesda, MD
- Ann Dean, PhD, Gene Regulation & Development, Section, NIDDK, Bethesda, MD
- Emery Bresnick, PhD, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI
- Keji Zhou, PhD, Immunology Center, NHLBI, Bethesda, MD
- Nan-ping Weng, PhD, Lymphocyte Differentiation Section, NIA, Baltimore, MD
- Remy Bosselut, PhD, Laboratory of Immune Cell Biology, NCI, Bethesda, MD
Contact
For more information, email lovep@mail.nih.gov.


