Regulation of Mammalian Cell Proliferation and Differentiation

- Melvin L. DePamphilis, PhD, Head, Section on Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
- Kotaro Kaneko, PhD, Staff Scientist
- Alex Vassilev, PhD, Staff Scientist
- Diane Adler-Wailes, MS, Senior Research Assistant
- Xiaohong Zhang, BA, Technical Assistant
- Yi-Yuan Huang, PhD, Visiting Fellow
- Courtney Kurtyka, PhD, Visiting Fellow
- Gaurav Sharma, PhD, Visiting Fellow
Nothing is more fundamental to living organisms than the ability to reproduce. Each time a human cell divides, it must duplicate its genome, a problem of biblical proportions. A single fertilized human egg contains 2.1 meters of DNA. An adult of about 75 kg (165 lb) consists of about 29 trillion cells containing a total of about 60 trillion meters of DNA, a distance equal to 400 times the distance from Earth to sun. Not only must the genome be duplicated trillions of times during human development, but it must be duplicated once and only once each time a cell divides (termed mitotic cell cycles). If we interfere with this process by artificially inducing cells to re-replicate their nuclear genome before cell division, the result is DNA damage, mitotic catastrophe, and programmed cell death (apoptosis). On rare occasions, specialized cells can duplicate their genome several times without undergoing cell division (termed endocycles), but when this occurs, it generally results in terminally differentiated polyploid cells, which are viable but no longer proliferate. As we age, however, the ability to regulate genome duplication diminishes, resulting in genome instability, which allows genetic alterations that can result in promiscuous cell division—better known as cancer. For a comprehensive description of genome duplication in all forms of life, refer to DePamphillis ML, Bell SD. Genome Duplication, Garland Science, 2010; DNA Replication. Eds. Mechali M, DePamphilis ML. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2013).
Our research program focuses on three questions. What are the mechanisms that restrict genome duplication to once per cell division? How are these mechanisms circumvented to allow developmentally programmed induction of polyploidy in terminally differentiated cells? How can we manipulate these mechanisms to destroy cancer cells selectively?
Regulation of DNA replication in mammalian cells
Genome duplication begins when the six-subunit origin recognition complex (ORC) binds to specific chromosomal loci termed origins of bidirectional replication, which we and others have mapped at specific sites in the genomes of flies and mammals. The sites are determined by both genetic and epigenetic features. The number and location of replication origins in the cells of multicellular organisms can change from an average of one in every 10 to 20 kb in the rapidly cleaving embryos of frogs, flies, and fish to one in every 50 to 300 kb in the differentiated cells of adult organisms. Developmental changes in origin density also occur during specific stages in animal development. Thus, metazoan genomes contain many potential replication origins but, during development, some of these sites are selectively activated while others are suppressed, a concept introduced many years ago as the "Jesuit Model", because many are called, but few are chosen (DePamphilis ML, Ann Rev Biochem 1993;62:29; Curr Opin Cell Biol 1993;5:434; J Biol Chem 1993;268:1).
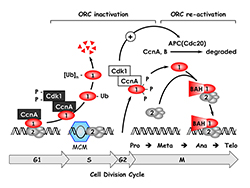
Click image to enlarge.
Figure 1. The ORC cycle in mammalian cells (see Noguchi et al. EMBO J 2006;25:5372 and references therein)
ORC(1–6) is bound to chromatin during the G1 phase of the cell cycle, at which time it is part of a prereplication complex. When S phase begins, the association between Orc1 and chromatin-bound ORC(2–6) is destabilized by selective CDK–dependent phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Monoubiquitinated Orc1 is exported to the cytoplasm. The remaining ORC subunits are subsequently released from chromatin. Polyubiquitinated Orc1 is degraded by the 26S proteasome. Orc1 levels are restored during the G2-to-M transition, but Orc1 is hyperphosphorylated, an event that prevents ORC assembly. During the anaphase-to-G1 phase transition, Orc1 is dephosphorylated and, together with other ORC subunits, binds to chromatin, an event facilitated by the Orc1 BAH domain, a protein/protein interaction domain involved in gene silencing. If Orc1 is not associated with other ORC subunits, or if it is not phosphorylated or ubiquitinated, it induces apoptosis.
The ORC initiates assembly of prereplication complexes (preRCs) consisting of a DNA helicase loader [ORC(1–6) and replication factors Cdc6 and Cdt1] and the replicative DNA helicase [Mcm(2–7)]. Several years ago, we discovered that the behavior of ORC in mammalian cells differs significantly from that in single-cell eukaryotes such as yeast. In contrast to yeast, Orc1 associates weakly with the stable core complex ORC(2–5), and the ability of ORC to initiate DNA replication depends on this interaction. Moreover, it appears that the interaction of Orc1 with ORC(2–5) is one of the mechanisms that regulate when and where initiation events occur. We termed this concept the ORC cycle, and we and others have established its basic features (Figure 1). Cell cycle–dependent modifications of Orc1 regulate Orc1 activity, and Orc1 activity regulates ORC activity, which regulates initiation of DNA replication.
The ORC cycle is only one of six known mechanisms that can determine when and where DNA replication begins in human cells. Cdk2•CcnA (cyclin-dependent kinase-2•cyclin A) also suppresses Cdc6 (cell vision cycle-6) and Cdt1 (chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor-1) activities by phosphorylation, and Cdt1 is targeted by two ubiquitin ligases and by geminin, a Cdt1–specific protein inhibitor (Figure 2). However, not every pathway is active in all cell types. For example, cells derived from human cancers are dependent on geminin to prevent DNA re-replication, whereas cells derived from normal human tissues are dependent on both geminin and cyclin A–dependent CDK (cyclin-dependent kinase) activity.
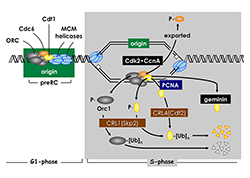
Click image to enlarge.
Figure 2. Several convergent pathways restrict genome duplication to once per cell division.
In human cells, activity of the replication factor Cdt1 is down-regulated in four ways. Free Cdt1 is phosphorylated by Cdk2 in association with cyclin A (CcnA), thereby suppressing Cdt1 activity and converting Cdt1 into a substrate for the CRL1Skp2 ubiquitin ligase. As replication forks pass through the origin, Cdt1 binds to the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) clamp, which holds the replicative DNA polymerase onto the replication fork. The Cdt1•PCNA•chromatin form of Cdt1 is a substrate for the CRL4Cdt2 ubiquitin ligase. Ubiquitinated Cdt1 is then degraded by the 26S proteasome. Finally, geminin binds to Cdt1 and inhibits its activity. In addition to inactivation of Cdt1, CcnA–dependent phosphorylation of Orc1 prevents it from binding to chromatin during mitosis, and CcnA–dependent phosphorylation of Cdc6 suppresses its activity and promotes its nuclear export.
A rare event in mammals, endoreduplication, by which the nuclear portion of the genome is duplicated one or more times (endocycles) without an intervening mitosis, is a common event among arthropods and plants. In mammals, it first occurs during peri-implantation development when cells within the trophectoderm (TE) of the blastocyst are deprived of the mitogenic factor FGF4 (fibroblast growth factor-4). Trophoblast stem (TS) cells then differentiate into the polyploid, viable, non-proliferating trophoblast giant (TG) cells required for embryo implantation and placentation (Figure 3). PreRC assembly requires the absence of both CDK activity and geminin, a condition that occurs in mitotic cell cycles during the anaphase-to-G1 phase transition. We discovered that this condition could be induced in TS cells by selective chemical inhibition of CDK1, the enzyme required for entry into mitosis, but not in embryonic stem (ES) cells, in which the consequence is apoptosis. Therefore, selective inhibition of CDK1 triggers endoreduplication only in cells programmed to differentiate into polyploid cells. Similarly, FGF4 deprivation of TS cells induced expression of two CDK–specific inhibitors: p57/Kip2 and p21/Cip1. One (p57) was essential for endoreduplication while the other (p21) appeared to facilitate p57 activity by suppressing expression of Chk1 (checkpoint kinase-1) and the mitotic inhibitor Emi1 (Figure 4). TS cells (+FGF4) express both the p57 and p21 genes, but the non-activated form of Chk1 phosphorylates the p57 and p21 proteins, thereby targeting them for ubiquitin-dependent degradation. In TG cells, CHK1 is suppressed to allow p57 expression during G phase, CDK2 is required for DNA replication, and p57 is degraded during S phase to allow endocycles.
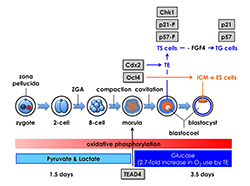
Click image to enlarge.
Figure 3. Mouse pre-implantation development: zygotic gene activation (ZGA) begins at the two-cell stage.
The eight totipotent blastomeres at the eight-cell stage compact into a morula, and transcription factors Tead4, Cdx2, and Oct4 mark the beginning of a chain of events that specifies the trophectoderm (TE) and inner cell mass (ICM). Oct4 is the first gene whose expression is essential for maintaining blastomeres in a totipotent state, thereby producing the ICM and embryonic stem (ES) cells that differentiate into embryonic tissues. Tead4 is the first gene whose expression is essential for differentiation of blastomeres into TE and trophoblast stem (TS) cells, which produce the placenta. In the absence of Tead4 expression, all totipotent blastomeres produce OCT4 protein, revealing that the TEAD4 protein is required for Cdx2 gene expression. However, TEAD4 is essential for blastocyst formation only under conditions that increase the rate of oxidative phosphorylation. Following compaction, pre-implantation embryos switch energy substrates from pyruvate and lactate to glucose in order to meet the increased energy demands of blastocoel formation, an event unique to the TE. Thus, Tead4 does not specify the TE; rather, TEAD4 maintains energy homeostasis so that other genes can specify the TE.
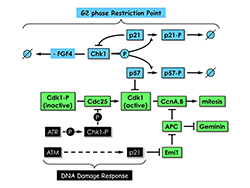
Click image to enlarge.
Figure 4. Proliferating trophoblast stem (TS) cells exhibit a G2 phase restriction point analogous to the G1 restriction point in proliferating cultured mammalian cells.
In the presence of the mitogen FGF4 and in the absence of DNA damage, Chk1, the same checkpoint kinase that is activated by DNA damage, phosphorylates both p57 and p21, thereby targeting them for ubiquitin-dependent degradation. In the absence of FGF4 and DNA damage, Chk1 expression is suppressed by an as yet unidentified mechanism. Both p57 and p21 proteins accumulate; p57 inhibits CDK1, and TS cells exit their mitotic cell cycle and differentiate into trophoblast giant (TG) cells; and p21 plays several roles, including suppressing Chk1 expression to maintain TG cell status and inhibiting Emi1 to activate the anaphase-promoting complex (APC), which promotes prereplication complex (preRC) assembly by targeting cyclins A and B and geminin for degradation. Both Chk1 and p21 are also components of the DNA–damage response that prevents mitosis until the problem is corrected; the features that distinguish their roles in the two regulatory mechanisms remain to be elucidated.
DNA replication and cell differentiation during pre-implantation development
Fertilization activates the first round of genome duplication, after which the fertilized egg cleaves into a two-cell embryo (Figure 3). In mice, the two-cell embryo then activates expression of about 300 genes that are required to continue development of the organism (termed zygotic gene activation). Initially, every cell (blastomere) produced by the cleavage events is 'totipotent,' that is, it is capable of giving rise to the entire organism. But, within five rounds of cell cleavage, a blastocyst appears, marking the beginning of cell differentiation. The blastocyst consists of a spherical monolayer of epithelial cells called the TE that gives rise to TS cells, TG cells, and eventually to the placenta. The TE layer encompasses a group of cells called the inner cell mass, which gives rise to ES cells and eventually to the embryo.
For some years, our goal has been to determine whether the requirements for genome duplication in cultured cells are the same for cleavage-stage embryos, for the stage prior to cell differentiation, and for the transition from mitotic cell cycles to endocycles. To this end, we identified genes that we thought might be critical for pre-implantation development. The results have been fruitful, but surprising. We discovered that Dkkl1, a gene unique to mammals, is expressed specifically during implantation of the embryo and development of spermatocytes into sperm. Moreover, we showed that inactivation of Dkkl1 in mice resulted in the production of sperm that are defective in fertilization. We discovered that Tead2, the gene encoding one of a highly conserved family of four transcription factors that share a common DNA–binding domain, is expressed from the two-cell embryo throughout pre-implantation development but, remarkably, is not required until after implantation and the start of nervous system formation. Mice lacking a functional Tead2 gene have difficulty forming a neural tube. Failure to close the neural tube in mice is called exencephaly, which is related to anencephaly, the common human birth defect that can be prevented by folic acid. We also discovered that Tead2 and Tead4 are the only Tead genes expressed in pre-implantation mouse embryos and that, in contrast to genetic inactivation of Tead2, genetic inactivation of Tead4 results in the formation of a morphologically abnormal morula, the absence of TE–specific genes, and failure to produce a blastocoel. These and other results in the literature strongly suggested that Tead4 is a master gene that sets in motion the first round of cell differentiation during mammalian development. Surprisingly, our subsequent research demonstrated otherwise.
Master genes trigger a sequence of events that specify cell fate. However, genes essential for maintaining a metabolic state that allows other genes to specify cell fate may be mistaken for master genes. We validated the concept by showing that Tead4, the presumptive master gene for trophectoderm specification, is a homeostatic gene that is essential for blastocoel formation in utero, a prerequisite for embryo implantation and placentation. Requirement for Tead4 is induced metabolically, not developmentally, and conditions that minimize oxidative stress allow embryos lacking TEAD4 to develop into blastocysts expressing genes required to produce functional trophectoderm. TEAD4, which is expressed at the eight-cell stage, is essential only under conditions that promote energy production by oxidative phosphorylation (Figure 3). Given that either inhibition of the mTOR pathway or an anti-oxidant alleviates the requirement, TEAD4 appears to regulate changes in redox potential that are expected to occur during the high levels of oxidative phosphorylation associated with blastocyst formation in utero (Kaneko and DePamphilis, Development 2013;140:3680).
And-1 coordinates with Claspin for efficient Chk1 activation in response to replication stress.
The replisome is important for DNA replication checkpoint activation, but how specific components of the replisome coordinate with ATR, a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that is involved in sensing DNA damage and activating the DNA damage checkpoint, to activate Chk1 in human cells remains largely unknown. We demonstrated that And-1, a replisome component, acts together with ATR to activate Chk1. And-1 is phosphorylated at T826 by ATR following replication stress, and the phosphorylation is required for And-1 to accumulate at the damage sites, where And-1 promotes the interaction between Claspin and Chk1, thereby stimulating efficient Chk1 activation by ATR. Significantly, And-1 binds directly to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and facilitates the association of Claspin with ssDNA. Furthermore, And-1 associates with replication forks and is required for the recovery of stalled forks. These studies establish a novel ATR–And-1 axis as an important regulator for efficient Chk1 activation and reveal a novel mechanism whereby the replisome regulates the replication checkpoint and genomic stability.
Geminin is essential to prevent DNA re-replication–dependent apoptosis in pluripotent cells, but not in differentiated cells.
Geminin is a dual-function protein unique to multicellular animals with roles in modulating gene expression and preventing DNA re-replication. We showed that geminin is essential at the beginning of mammalian development to prevent DNA re-replication in pluripotent cells, exemplified by ES cells, as they undergo self-renewal and differentiation. We characterized ES cells, embryonic fibroblasts, and immortalized fibroblasts before and after geminin was depleted either by gene ablation or small interfering RNA (siRNA). Depletion of geminin under conditions that promote either self-renewal or differentiation rapidly induced DNA re-replication, followed by DNA damage, then a DNA damage response, and finally apoptosis. Once differentiation had occurred, geminin was no longer essential for viability, although it continued to contribute to the prevention of DNA damage induced by DNA re-replication. We detected no relationship between expression of geminin and genes associated with either pluripotency or differentiation. Thus, the primary role of geminin at the beginning of mammalian development is to prevent DNA re-replication–dependent apoptosis, a role previously believed essential only in cancer cells. The results suggest that regulation of gene expression by geminin occurs only after pluripotent cells differentiate into cells in which geminin is not essential for viability.
Identification of genes that are essential to restrict genome duplication to once per cell division
The mechanism that duplicates the nuclear genome during the trillions of cell divisions required to develop from zygote to adult is the same throughout the eukarya, but the mechanisms that determine where, when, and how much nuclear genome duplication occurs differ among the eukarya. They allow organisms to change the rate of cell proliferation during development, to activate zygotic gene expression independently of DNA replication, and to restrict nuclear DNA replication to once per cell division. They allow specialized cells to exit their mitotic cell cycle and differentiate into polyploid cells and, in some cases, to amplify the number of copies of specific genes. It is genome duplication that drives evolution, by virtue of the errors that inevitably occur when the same process is repeated trillions of times. They are, unfortunately, the same errors that produce age-related genetic disorders such as cancer.
Nuclear genome duplication is normally restricted to once per cell division, but aberrant events that allow excess DNA replication (EDR) promote genomic instability and aneuploidy, both of which are characteristics of cancer development. We provided the first comprehensive identification of genes that are essential to restrict genome duplication to once per cell division. We screened an siRNA library of 21,584 human genes for those that prevent EDR in cancer cells with undetectable chromosomal instability. We validated candidates by testing multiple siRNAs and chemical inhibitors on both TP53+ (tumor protein p53) and TP53– cells to reveal the relevance of this ubiquitous tumor suppressor in preventing EDR, and in the presence of an apoptosis inhibitor to reveal the full extent of EDR. The results revealed 42 genes that prevented either DNA re-replication or unscheduled endoreplication. They all participate in one or more of eight cell-cycle events. Seventeen had not been identified previously in this capacity. Remarkably, 14 of the 42 genes have been shown to prevent aneuploidy in mice. Moreover, suppressing a gene that prevents EDR increased the ability of the chemotherapeutic drug Paclitaxel to induce EDR, suggesting new opportunities for synthetic lethalities in the treatment of human cancers.
Publications
- Huang YY, Kaneko KJ, Pan H, DePamphilis ML. Geminin is essential to prevent DNA re-replication-dependent apoptosis in pluripotent cells, but not in differentiated cells. Stem Cells 2015;33(11):3239-3253.
- Hao J, de Renty C, Li Y, Xiao H, Kemp MG, Han Z, DePamphilis ML, Zhu W. And-1 coordinates with Claspin for efficient Chk1 activation in response to replication stress. EMBO J 2015;34:2096-2110.
- Vassilev A, Lee CY, Vassilev B, Zhu W, Ormanoglu P, Martin SE, DePamphilis ML. Identification of genes that are essential to restrict genome duplication to once per cell division. Oncotarget 2016;7:34956-34976.
- DePamphilis ML. Genome duplication: the heartbeat of developing organisms. Curr Top Dev Biol 2016;116:201-229.
- DePamphilis ML. Genome duplication at the beginning of mammalian development. Curr Top Dev Biol 2016;120:55-102.
- DePamphilis, ML (Editor). Mammalian Preimplantation Development. Curr Top Dev Biol 2016;120:1-478.
Collaborators
- Scott E. Martin, PhD, NIH Chemical Genomics Center, NHGRI, Rockville, MD
- Wenge Zhu, PhD, George Washington University Medical School, Washington, DC
Contact
For more information, email depamphm@mail.nih.gov or visit http://depamphilislab.nichd.nih.gov.


